Writing this article in the year 2020 most of us can agree that we have never had as much access to information as we do today, readily available at our fingertips. The technology that we are using to access and use this information is evolving so quickly that according to the law of accelerating returns, the pace of information technology progress will speed up exponentially over time, this is because there is a common force driving it forward. Being exponential, as it turns out, is all about evolution.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The ever increasing abilities of machines to learn and act intelligently will continue to absolutely transform our world. AI is also the main driving force behind many of the other trends on this list. Overall Global spending on AI is projected to hit $46bn by the end of 2020 and this trend is expected to grow significantly into the future.

Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things refers to the billions of physical devices both mechanical and digital, provided with unique identifiers (UIDs) that have the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human interaction. Connecting up all of these devices and adding sensors to them adds a level of digital intelligence to devices that would be otherwise dumb, this enables them to communicate real-time data without involving a human being.

The main concept of a network of smart devices was discussed as early as 1982, with a modified Coca-Cola vending machine at Carnegie Mellon University becoming the first Internet-connected appliance
Just how big is the Internet of things?
There are already much more internet-connected devices in the world than there are people. The technology analyst company IDC predicts that in total there will be 41.6 billion connected IoT devices by 2025. They have also suggested that industrial and automotive equipment represent the largest opportunity of connected “things,” but, right now we are seeing strong adoption of smart home and wearable devices in the near term.
Natural Language Processing
While natural language processing isn’t new, the technology behind NLP is advancing rapidly thanks to an increased interest in human-to-machine communications, this, coupled with the availability of big data, powerful computing, and enhanced algorithms.
Natural language processing (NLP) is a branch of artificial intelligence that helps computers understand, interpret, and manipulate human language. NLP draws from many disciplines, including computer science and computational linguistics, in its pursuit to fill the gap between human communication and computer understanding.

Digital Twins
For a simple explanation, a digital twin is a virtualised model of a process, product, or service. The pairing of both the virtual and physical worlds allows the analysis of data and the monitoring of systems to help identify problems before they even occur, this, in turn, prevents downtime, develops new opportunities and even plans for the future by using simulations.

The first implementation of a Digital Twin took place in 2002 at the University of Michigan’s Society of Manufacturing Engineers, since then, a lot has changed. This generations digital twins allow you to not only model and visualise a business asset, but also to make predictions, take actions in real-time, and use current technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to augment and act on your data in very clever ways.
Cloud and Edge computing
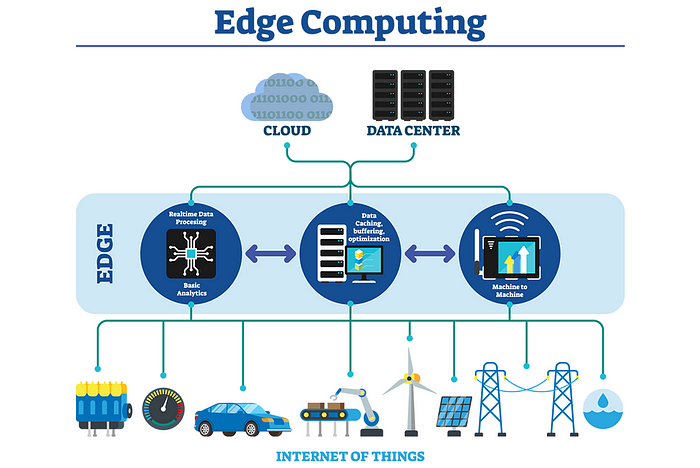
The construction of the internet as we know it was not designed to handle the traffic flows of today, and it’s only going to get more congested in the coming years. Traditionally, the internet’s traffic flows have largely been download-centric and the network infrastructure has been built out to support those types of traffic flows. In modern times, however, the gravity of data and compute has shifted from the core to the edge as a result of technologies like the Internet of Things(IoT), Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, HD streaming, and Cloud Gaming. From the inception of the internet, there has never been more content and data that is now being created, processed, and stored at the edge. This modern dynamic is creating enormous network and traffic bottlenecks.
As a result, the future of our digital economies depends largely on edge data centres, These localised data centres will alleviate these bottlenecks by enabling the multi-directional traffic flows to occur through the peering and smart routing of traffic at the edge.
In many cases, it is incredibly beneficial to handle data on the device where it’s generated. That’s where edge computing comes in. Edge computing helps decentralise data processing and lowers dependence on the cloud.
Edge computing has several advantages, such as:
- Reducing latency
- Responsive application performance
- Increasing data security and privacy
- Conserving network and computing resources
- Reducing operational costs
Edge data centres help us to rearchitect the internet in a way that supports the massive flood of data and traffic flows that are being generated by technologies like AI, IoT, cloud gaming, and HD streaming video.